If you are a freelancer, you are just like a business owner who at some point needs to file an IRS Schedule C.
Here is our article on Form 1040 – Schedule C, who has to file and several tips on how to file Schedule C.
What is Schedule C?
IRS schedule C is a tax form which is used for reporting profits and loss. You fill this out at tax time and you file it electronically together with Form 1040.
Schedule C is for those who opreate sole proprietorships, or those who have single owner small businesses.
Take note, Schedule C is not the same as a 1099 Form, although you may need your 1099-NEC to fill out your Schedule C.
Who files a schedule C?
Schedule C is for 2 types of business owners:
Sole proprietorsSingle member limited liability corporations
Take note that Schedule C is not for C corporations or S corporations.
Sole proprietorships are unincorporated businesses, typically they are ran by a single person and they take all the profits and yet they garner all losses and liabilities. They are often the choice of business model for freelancers those who have a side gig, independent contractors or those who operate small businesses.Single member limited liability corporations are owned by a single person.
Sometimes there is no distinction between the owner and corporation so income and profits are calculated to the owner’s tax return.Day jobs
You may also have to file a Schedule C if you have a regular day job and you’re someone’s employee. If you’re freelancing, your self-employment may suggest you need to add a Schedule C in your tax filing. IRS considers you a business if your gig is a regular thing and you continually and regularly make money from it.What is on a Schedule C?
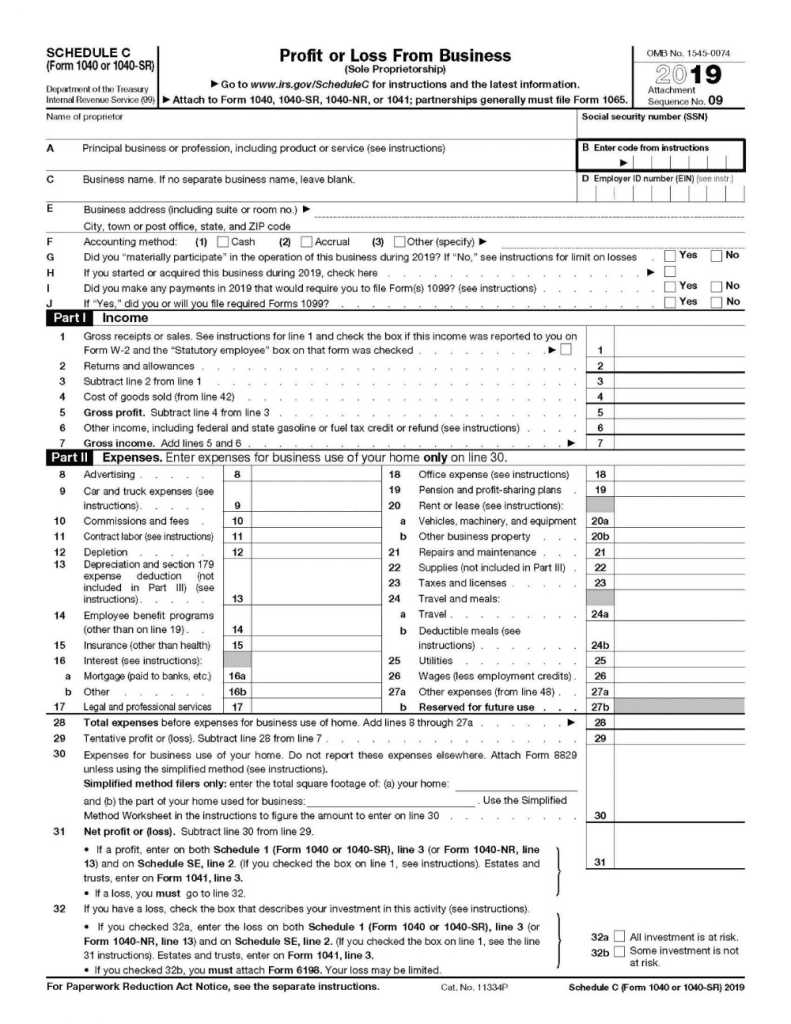
Schedule C is a place to report revenues from your business. This is also all the types of expenses you incur to run your business. Your business income minus your expenses is also your net profit as income on your Form 1040. How to fill out Schedule C
Your form typically consists of your income statement and balance sheet, receipts for spending related to business, your inventory and mileage records used for business.
-
Part 1 is the tally of sales and report of the cost of goods sold, in short it is your gross profit.
-
Part 2 is your business expenses. There are many categories including advertising, legal, rent, travel and other costs. You have to add all these expenses and subtract them from your gross profit which will then result on your net profit.
-
Your initial net profit is taxable for your tax return. If you have net loss, it can be deductible from your personal tax return.
-
Part 3 helps you calculate your sales.
-
Part 4 is infromation on a vehicle or if you have car or auto related business spending.
How to Speed up your Schedule C filing
Create a pay stub
Create a pay stub to record your income and make sure you’re tracking your earnings pre taxes. If it comes to tax season your filing will be much easier and you can easily fill in your spending vs your revenues.
Fill out multiple schedule C’s
It’s a single Schedule C per side gigs. So if you have 2 side gigs, you may need to fill out 2 schedule C’s to report your earnings.
Take advantage of other tax deductions
These include car expenses and travel and business related meal expenses. Make sure to track what tax relief you can get so that you won’t have to overspend with the IRS.
Keep track of your other taxes.
If you have received commissions or rents and other miscellaneous income, you may need to file 1099-MISC. If you’re only freelancing, then use 1099-NEC, prepping all your other tax forms is paramount and it will help you file your taxes sans all the hassle.
